What is the rack and pinion gear assembly?
The rack and pinion gear assembly is a crucial component of modern vehicle steering systems, widely used in most front-wheel-drive vehicles, as well as some rear-wheel-drive and all-wheel-drive models. As a mechanical structure that directly transmits power, its simple yet efficient working principle provides the driver with a smooth and precise steering experience.
Understanding the working principle, function, structure, and application of the rack and pinion gear assembly will help vehicle owners or technicians better understand this critical component and ensure the proper functioning of the steering system.
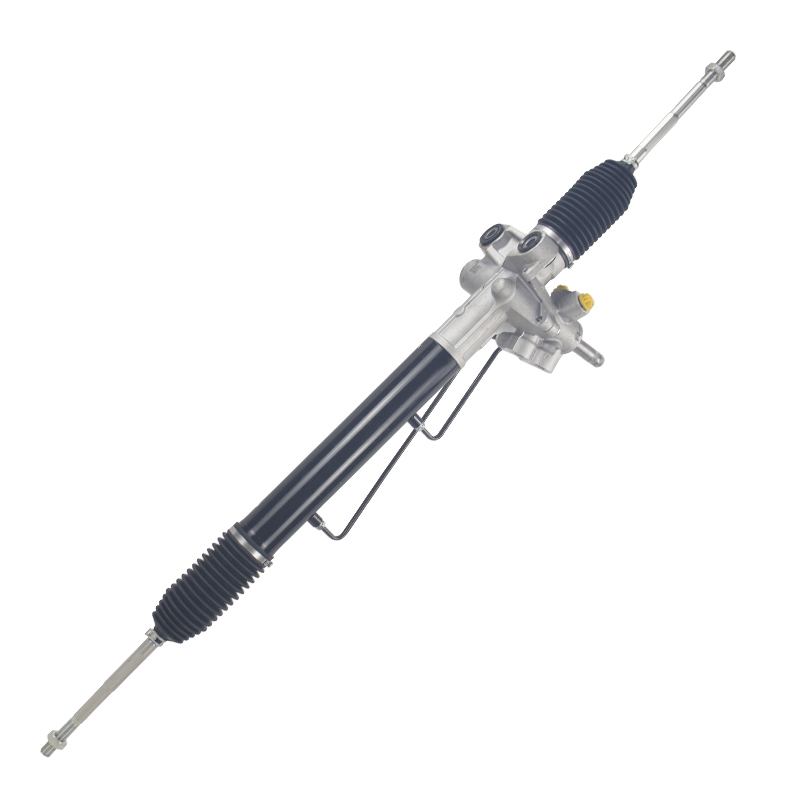

What is the rack and pinion gear assembly?
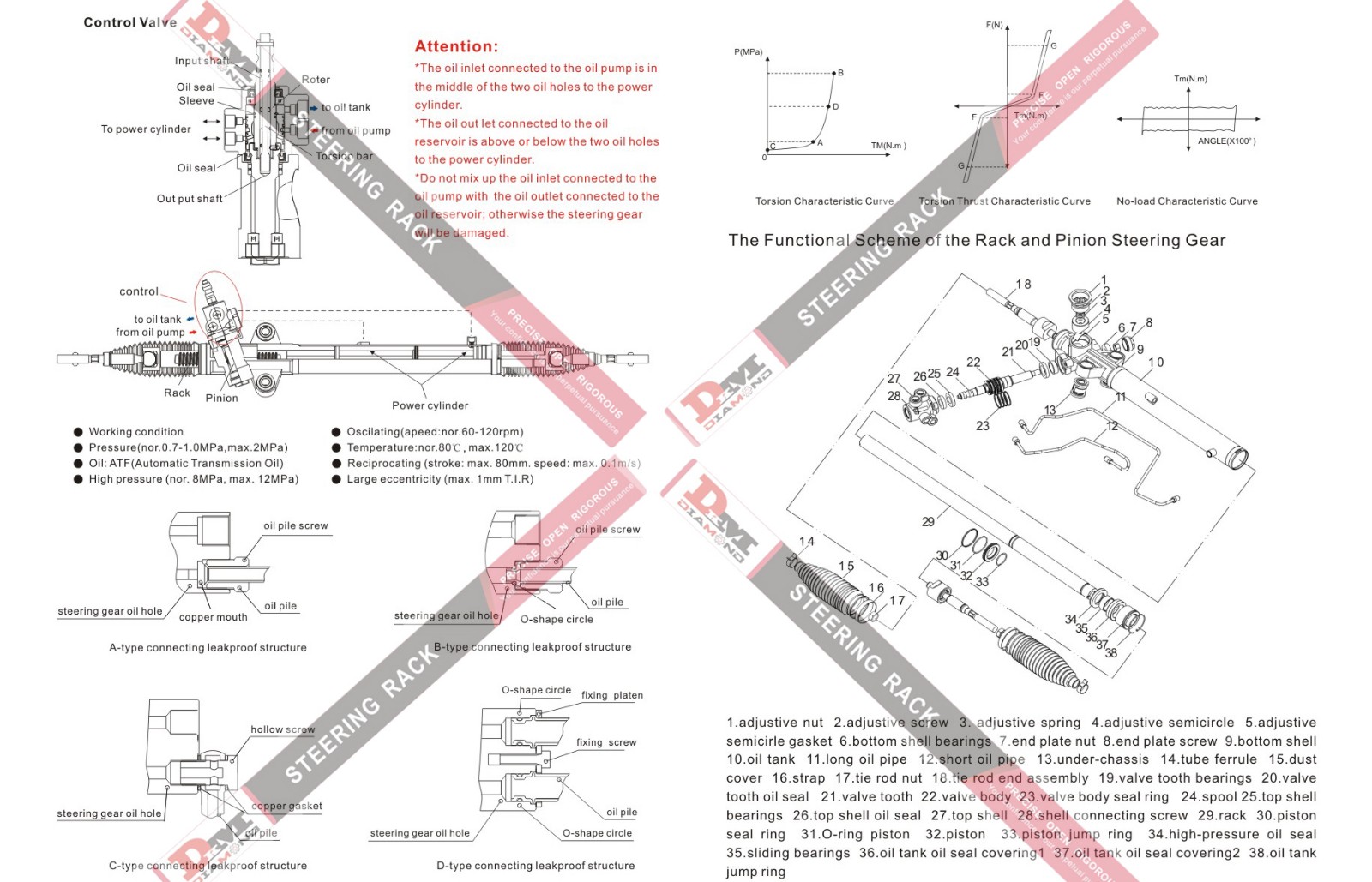
The rack and pinion gear assembly is a complete device consisting of two parts: a rack and a pinion. Specifically, the rack is a straight gear with a row of evenly spaced teeth, typically in a straight configuration; the pinion is a round gear with a tooth profile that matches the rack. The rack is typically mounted to the steering system's frame, while the pinion is connected to the driver through the steering wheel.
During steering, rotation of the steering wheel is transmitted to the pinion through the steering column. The pinion drives the rack left and right, thereby steering the wheels. This system utilizes the meshing principle of gears to convert circular rotation into linear propulsion, resulting in smoother and more precise steering.
How does the rack and pinion gear assembly work?
The working principle of the rack and pinion gear assembly can be simply divided into the following steps:
· Steering wheel rotation: The driver changes the vehicle's direction by turning the steering wheel. The steering wheel is connected to the pinion gear via the steering column.
· Pinion rotation: When the driver turns the steering wheel, the steering wheel rotates the steering column, which in turn drives the pinion gear. The pinion gear is typically fixed to one end of the steering column.
· Linear motion of the rack: The rotation of the pinion gear meshes with the rack gear, converting rotational motion into linear motion, causing the rack gear to move along its length.
· Steering wheel: The movement of the rack gear, through a linkage system or a steering arm directly connected to the wheel, causes the wheel to rotate accordingly, completing the steering process.
In this process, the design precision of the rack and pinion gear directly determines the steering sensitivity and precision. By adjusting the tooth profile, clearance, and material of the rack and pinion gear, steering feel and operating comfort can be optimized.

What are the structural components of a rack and pinion gear assembly?
The rack and pinion gear assembly is relatively simple, yet it incorporates several key components that work in harmony to ensure smooth and efficient steering. The following are the main components of a rack and pinion gear assembly:
1. Rack:
A rack is a long, straight-lined component with teeth. The rack's length varies depending on the vehicle's design, and it typically connects to other components in the steering gear, such as the power steering system. The rack's teeth mesh with those of a pinion gear, transmitting power to the wheels.
Rack teeth can be straight, helical, or curved, with straight teeth being more common due to their ease of production and low cost. Racks are typically made of high-strength steel or alloy to ensure sufficient strength and durability.
2. Pinion:
The pinion gear is another core component in the rack and pinion gear assembly. Its teeth match those of the rack and are typically round. It is mounted at the end of the steering column. The size and number of teeth on the pinion gear determine the steering precision and sensitivity. The pinion gear can have either straight or helical teeth. Helical gears are commonly used in high-performance vehicles, offering greater precision and smoothness.
The pinion gear is typically constructed of high-strength steel or alloy to enhance wear and impact resistance.
3. Support and Sealing Devices:
To ensure smooth movement of the rack and pinion gears and prevent dust, moisture, and other particles from entering the system, the rack and pinion gear assembly is equipped with support and sealing devices. The support device typically supports the rack and ensures linear motion within the system, while the seal prevents lubricant leakage and external contaminants.
4. Lubrication System:
Because the rack and pinion gear assembly experiences significant friction and pressure during operation, lubricant plays a crucial role. Lubricant not only reduces friction and increases the lifespan of the rack and pinion gear, but also helps cool the system and prevent overheating.

What are the advantages and disadvantages of a rack and pinion gear assembly?
Advantages of a rack and pinion gear assembly:
· Simple Structure: The rack and pinion gear assembly's relatively simple design makes it easy to manufacture and maintain, which is one of the reasons for its widespread use.
· Precise Response: Due to its mechanical transmission characteristics, rack and pinion gear assemblies provide more direct and precise steering feedback, reducing mechanical loss and delay.
· Cost-Effectiveness: Compared to other complex steering systems, rack and pinion gear assemblies have relatively low production costs, making them the preferred choice of most car brands.
· Compactness: This system is relatively compact, adaptable to various types of vehicles, especially compact models where space is a concern.
Disadvantages of Rack and Pinion Gear Assemblies:
· Heavy Steering Feel: For some large or heavy vehicles, rack and pinion systems may not provide sufficient steering assistance, resulting in a heavy steering feel. While modern hydraulic power steering (HPS) and electronic power steering (EPS) effectively address this issue, rack and pinion systems still present this problem in some older vehicles or lower-end models.
· Wear Issues: Long-term use can cause wear on the meshing teeth of the rack and pinion gear, affecting steering precision. Therefore, regular inspection and maintenance are necessary to ensure proper system operation. Noise Issues: Under high loads or at high speeds, rack and pinion systems may produce some noise, which can be unpleasant for some drivers.
Application of the rack and pinion gear assembly in various steering systems
Rack and pinion gear assemblies are widely used in various steering systems, including:
1. Traditional Mechanical Steering Systems
In early mechanical steering systems, the rack and pinion gear assembly served as the core component, directly driving the wheels for steering. Although this system is relatively simple, it is still used in most older vehicles.
2. Hydraulic Power Steering (HPS)
In hydraulic power steering systems, the basic function of the rack and pinion system remains unchanged, but a hydraulic pump and hydraulic fluid are added to reduce steering resistance and increase steering sensitivity. Hydraulic power steering makes steering easier, especially at low speeds, significantly improving driving comfort.
3. Electronic Power Steering (EPS)
Electronic power steering systems use an electric motor instead of a traditional hydraulic system to provide power, making the rack and pinion system more efficient. The use of EPS makes the system more compact and automatically adjusts the amount of steering assistance based on vehicle speed.
What makes your pricing so competitive?
Our pricing reflects the advantages of factory-direct production. With our in-house facility, experienced workforce of 201–500 staff, and high automation, we cut out middlemen and reduce overhead. Combined with a strong annual turnover of USD5–10million and high output levels, we pass on cost savings to clients.
Buyers can enjoy low-price, high-quality parts, competitive bulk quotes, and discounted promotions—all backed by a reputable Chinese manufacturer.




