What causes a rack and pinion gear to break?
In modern automotive steering systems, racks and pinions are vital components that share the critical task of transmitting the driver's steering force to the wheels. Racks and pinions used in automotive steering systems are usually made of high-strength materials to withstand the ever-changing loads and friction.
However, racks and pinions may fail or even break over long periods of use. This article will explore in detail the causes of rack and pinion gear breakage in automobiles, including design defects, material problems, excessive loads, insufficient lubrication, environmental factors, etc., to help readers better understand this complex issue.
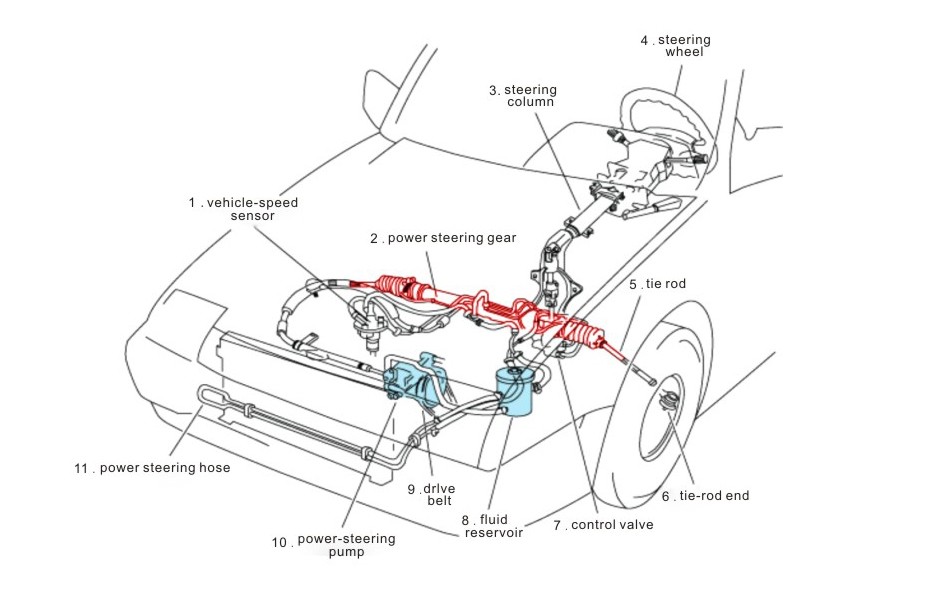
What is the role of racks and pinions?
In automotive steering systems, racks and pinions are the core part of the steering mechanism. The rack and pinion gear transmit the turning force from the steering wheel through precise meshing, thereby controlling the direction of the wheels. The rack is a toothed rod installed in the steering gear that is connected to the steering wheel and transmits rotational motion through the pinion. The pinion meshes with the rack and drives the rack to move back and forth in the horizontal plane, causing the wheels to turn.
Throughout the steering system, racks and pinions need to withstand large forces, especially when steering during driving, where repeated pressure and friction can put these components to great test. Because they are subject to large pressure and loads during steering, they need to have high durability in terms of design, materials, manufacturing processes, etc.

What are the causes of rack and pinion gear fracture?
Although racks and pinions show high reliability in normal use, they still face a variety of potential damage risks. The following are the main causes of rack and pinion gear fracture.
1. Design defects
The design of racks and pinions is a key factor in whether they can operate stably for a long time. If factors such as material strength, load distribution, and the working environment of the steering system are not considered during the design stage, racks and pinions may break during use. Common design defects include mismatched rack tooth profiles, incorrect meshing angles, and inappropriate meshing depths between racks and pinions. These design problems cause racks and pinions to bear uneven loads during operation, leading to stress concentration and ultimately fracture.
In addition, the size design of racks and pinions is also very important. Too large a rack may reduce the sensitivity of the steering system, while too small a rack may not be able to withstand excessive loads. Failure to properly calculate the load-bearing capacity during design will also increase the risk of rack and pinion gear fracture.
2. Material issues
Racks and pinions are usually made of high-strength alloy steel or other wear-resistant materials to ensure their durability in long-term use. However, if unqualified or low-quality materials are used during the production process, or the material synthesis process is not precise, the strength and wear resistance of the rack and pinion gear will be greatly reduced. Common material problems include:
· Insufficient material hardness: Insufficient material hardness will cause the rack and pinion gear to be unable to effectively withstand the huge pressure generated during work, and it is easy to crack or break.
· Uneven material: During the manufacturing process, the structure of the material may be uneven, resulting in low hardness in some parts and prone to fracture.
· Poor corrosion resistance: The steering system is exposed to a humid environment for a long time. If the material of the rack and pinion gear does not have good corrosion resistance, it is easy to cause material corrosion, thereby accelerating fracture.
3. Overload
The steering system may be overloaded in some extreme cases, causing the rack and pinion gear to break. Overload is usually caused by the driver turning the steering wheel suddenly and hard, or the vehicle is under extreme driving conditions (such as high speed, sudden braking, strong turning, etc.). This excessive load will cause excessive stress on the tooth surface of the rack and pinion, resulting in fatigue damage to the tooth surface and eventually causing fracture.
In addition, some parts in the steering system may have problems such as jamming or excessive friction, which will also cause the steering rack and pinion gear to bear pressure exceeding the design load. Long-term overload operation will cause cracks on the surface of the rack and pinion gear, which will then lead to fracture.
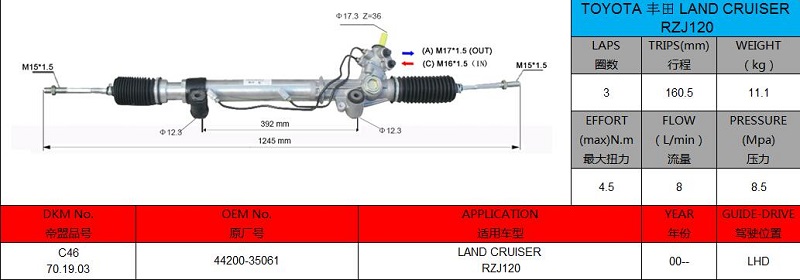
4. Insufficient lubrication
Lubrication is one of the key factors to ensure the long-term stable operation of the rack and pinion gear. If the lubrication is insufficient, the friction between the rack and pinion will increase dramatically, resulting in increased temperature, increased wear, and even cracks or fractures on the surface. The lubricant must not only be sufficient, but also kept clean to avoid dirt or impurities affecting the lubrication effect.
Especially in high temperature environments, the performance of the lubricant may decline, resulting in insufficient lubrication of the rack and pinion gear, which in turn increases the friction on the rack and pinion surface and increases the risk of fracture.
5. Fatigue damage
Fatigue damage is one of the common causes of rack and pinion fracture. Since the steering system needs to work for a long time, the rack and pinion gear will experience countless meshing and load changes. Long-term repeated stress will cause material fatigue and form microcracks, which will expand over time and eventually cause the rack and pinion to break. Especially in the absence of effective lubrication, fatigue damage occurs more quickly.
6. External environmental factors
External environmental factors, such as extreme temperature changes, rain, mud, salt water, etc., may accelerate the wear of racks and pinions and even cause them to break. In cold environments, the hydraulic oil in the steering system may become thicker, resulting in an increase in the workload of the steering system; in high temperature environments, the hydraulic oil may deteriorate, the lubrication effect will decrease, and the wear of racks and pinions will also be accelerated. In addition, salt water and moisture may accelerate corrosion, resulting in a decrease in material strength and an increase in the risk of fracture.
7. Improper installation
If the rack and pinion gear of the steering system are not properly aligned during installation, or excessive tightening force occurs during installation, this may cause uneven loads on the rack and pinion, resulting in breakage. In particular, when the meshing relationship between the pinion and the rack is improper, local excessive wear on the tooth surface will further lead to breakage.
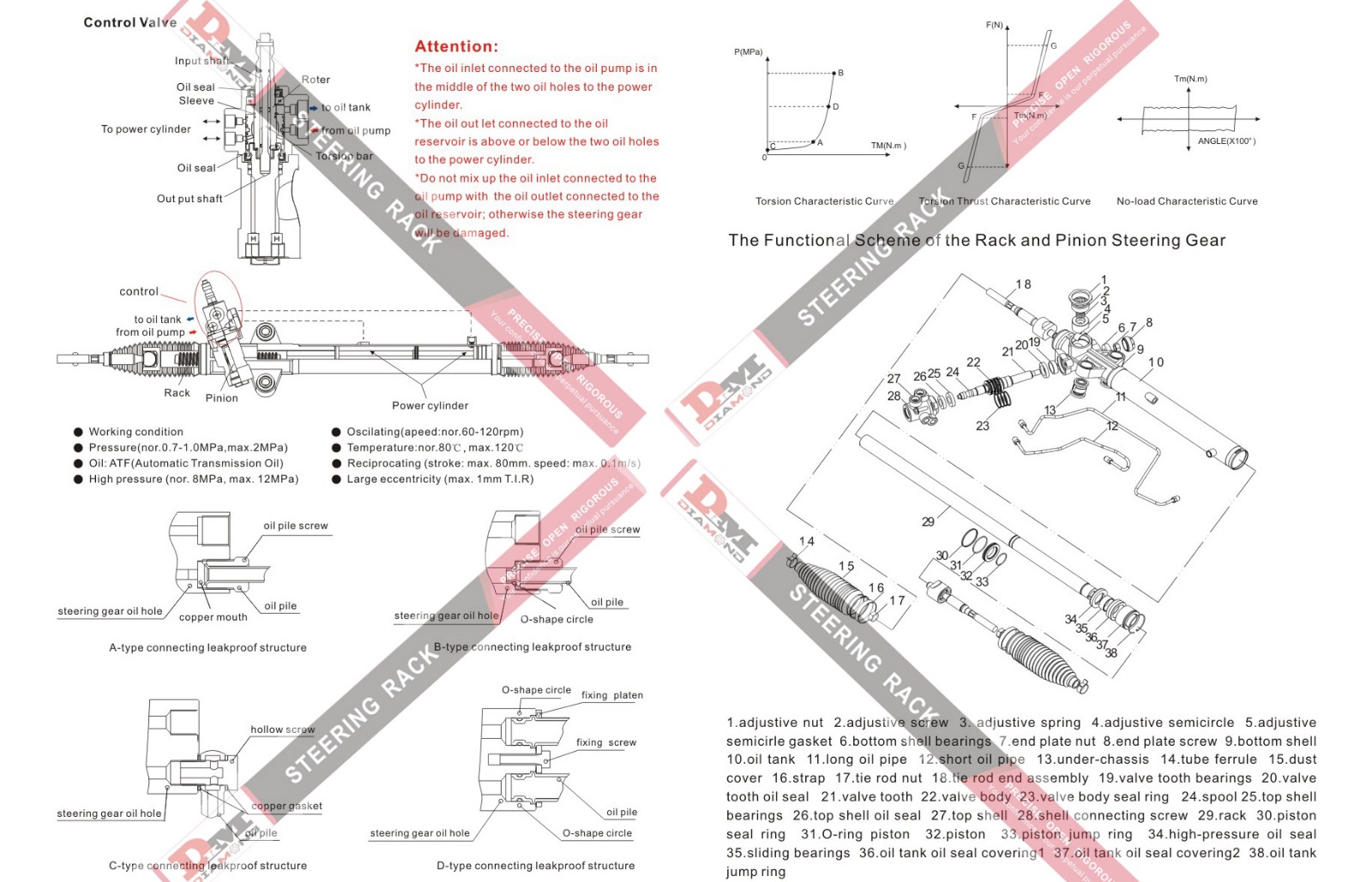
How to prevent rack and pinion gear breakage?
In order to reduce the risk of rack and pinion gear breakage, the following measures can be taken:
· Reasonable design: When designing the steering system, the size, material and tooth shape of the rack and pinion gear should be ensured to avoid excessive load or uneven tooth surface caused by inappropriate design.
· Select high-quality materials: Use high-strength, wear-resistant and corrosion-resistant materials to ensure that the rack and pinion gear can maintain high strength and durability in long-term use.
· Regular inspection and maintenance: Regularly check the steering system, especially the wear of the rack and pinion, and replace severely worn parts in time.
· Maintain good lubrication: Ensure that the steering system is fully lubricated to avoid excessive wear of the rack and pinion gear due to insufficient lubrication.
·Avoid excessive load: The driver should avoid sudden and forceful steering wheel movements and be careful not to drive under extreme conditions to reduce the risk of excessive load on the steering system.
·Avoid harsh environments: Try to avoid exposing the steering system to harsh environments, such as extreme temperatures, moisture, or corrosive substances.
Why choose DKM as your steering rack supplier?
DKM Company differentiates itself through over 25 years of manufacturing expertise, a well-equipped 20,000+m² facility with 280+ CNC and heat-treatment machines, and high automation. Our factory’s monthly output reaches 300,000 sets, ensuring prompt delivery at competitive prices.
We provide high-quality, CE/ISO-grade components and can offer bulk quotes, customized solutions, and discount promotions.
Whether you need OEM-standard parts for Toyota, Honda, etc., or cost-effective alternatives, DKM is a trusted China-based supplier and manufacturer.




