How should I decide the number of teeth for the rack and pinion steering mechanism?
As one of the most common steering systems in modern cars, the rack and pinion steering mechanism is widely used in steering wheel control of various models. It transmits the driver's steering action to the wheel through the meshing of the rack and the gear, thereby realizing the steering control of the vehicle.
The number of teeth plays a vital role in the rack and pinion steering mechanism. The choice of the number of teeth not only affects the steering accuracy, strength, response speed and control feel, but also has a profound impact on the reliability, durability and overall performance of the steering system.
Therefore, when designing or replacing the rack and pinion steering mechanism, it is particularly important to choose the number of teeth reasonably. Too many or too few teeth may lead to unsatisfactory system performance and even affect the safety of the vehicle.

What is the working principle of the rack and pinion steering mechanism?
The rack and pinion steering mechanism is a mechanical device that realizes steering control through the meshing of the gear and the rack. The rotation of the steering wheel is connected to the gear through the center column, and the gear then transmits the torque to the wheel through the meshing of its teeth and the rack, and finally realizes the steering of the vehicle.
In this process, there is a certain proportional relationship between the amount of steering wheel rotation and the amount of rack movement. The number of teeth on the gear, the length of the rack, and the meshing method between the rack and the gear will directly affect this ratio, and then affect the steering sensitivity, strength and comfort.
1. Steering wheel rotation and rack movement
When the driver turns the steering wheel, the steering wheel is connected to the gear through the center column, and the gear is connected to the rack through meshing. The movement of the rack drives the vehicle's bogie to turn the wheel. The relationship between the steering wheel's rotation angle and the wheel steering angle is determined by the number of teeth and structure of the gear and rack.
2. The influence of the number of teeth
The number of teeth directly affects the gear reduction ratio, that is, the ratio between the steering wheel rotation and the wheel steering. The more teeth the gear has, the higher the steering sensitivity, but the more effort required for steering; when the number of teeth on the gear is small, the steering force is small, but the steering sensitivity is low. This proportional relationship will have an important impact on the vehicle's controllability, the driver's control experience, and the accuracy of steering.

What is the impact of the number of teeth on the steering performance of the car?
The choice of the number of teeth is one of the key factors in designing a rack-and-pinion steering mechanism. Too many or too few teeth will affect the performance of the steering system. The following are the main effects of the number of teeth on steering performance:
1. Steering sensitivity
The number of teeth directly affects the rotation ratio between the steering wheel and the wheel. A larger number of teeth means that the gear can move the rack a certain distance with less rotation, which can improve the steering sensitivity. The driver only needs to turn the steering wheel slightly to make the wheel turn a large angle. This steering system is usually suitable for occasions that require quick response, such as sports cars and track vehicles.
However, a design with a large number of teeth also means that the torque required for steering is large, and the driver needs to apply more force to turn the steering wheel, which increases the difficulty of operation when driving at low speed or parking.
2. Steering comfort
Steering comfort refers to the feeling of the driver when operating the steering wheel. Too high or too low steering force will affect driving comfort. A design with fewer teeth will make steering easier because the transmission ratio of the rack-and-pinion is relatively small, and the driver needs to apply less force to achieve steering. However, too low a number of teeth may also lead to overly sensitive steering, especially when driving at high speeds, where a slight movement of the steering wheel may cause the vehicle to turn sharply, affecting the vehicle's stability.
Therefore, the appropriate number of teeth design should find a balance between steering sensitivity and steering comfort, so that the driver can get a proper sense of control when driving at high and low speeds.
3. Steering force
The number of teeth will affect the torque requirements of the steering system. A gear design with fewer teeth will result in a smaller torque when steering, so the driver has a lighter burden when operating the steering wheel. But a design with fewer teeth also means that the steering sensitivity is lower, and the driver needs to turn the steering wheel at a larger angle to make the wheels turn accordingly.
In contrast, when the number of teeth is larger, the torque required for gear meshing is larger, and the steering force will increase accordingly. Although a design with more teeth can bring higher steering accuracy and sensitivity, it also requires the driver to exert more effort.
4. Control accuracy
The accuracy of the steering system is directly related to the stability and safety of the vehicle. A design with more teeth will provide higher accuracy because it can drive the wheels to produce a smaller steering angle with a smaller steering wheel rotation. This design is particularly important for vehicles that require highly precise control, such as high-performance vehicles or vehicles with high precision requirements.
However, too many teeth may make the steering too sensitive, affecting the driver's control of the steering wheel, especially when driving at high speeds, which may lead to overly sensitive reactions. Too few teeth may lead to insufficient steering precision and affect controllability.

How to choose the number of teeth for the rack and pinion steering mechanism?
There is no fixed standard for choosing the appropriate number of teeth design. It usually requires comprehensive consideration of various factors such as different types of vehicles, uses, driving habits, and design goals. The following are several factors that need to be considered when choosing the number of teeth:
1. Vehicle type and use
Different types of vehicles have different requirements for the steering system. For example, for high-performance vehicles such as sports cars and sports cars, higher steering sensitivity and precision are usually required. At this time, choosing gears with more teeth can better meet the requirements. For ordinary family cars or SUVs, a moderate number of teeth design can provide good steering comfort and a more sensitive control experience.
2. Driving habits and needs
The driver's driving habits will also affect the choice of teeth. If the driver is used to more intense driving, he may tend to choose a design with more sensitive steering. At this time, it is more appropriate to choose a gear with more teeth. For vehicles driven in daily cities, drivers may prefer easier and more comfortable steering. Appropriately reducing the number of teeth may bring a better driving experience.
3. Design requirements of the steering system
When designing a steering system, it is necessary to select the number of teeth according to the overall design requirements of the steering system. For example, the design goal may require better stability and controllability at high speeds. At this time, a moderate number of teeth will be more appropriate. If the design goal requires the vehicle to be easier to control at low speeds, a design with fewer teeth can be selected.
4. Driving performance and road conditions of the vehicle
Different road conditions and driving performance will also affect the choice of the number of teeth. For example, for off-road vehicles or commercial vehicles that require frequent steering, a design with fewer teeth may be required to provide better controllability and driving comfort at low speeds and complex road conditions. For vehicles on highways, more teeth may be required to improve control accuracy and response speed.
5. Balance steering comfort and control performance
Among all design requirements, balancing steering comfort and control performance is the most critical. Too many teeth will make the steering too sensitive, which may affect the vehicle's stability at high speeds; too few teeth will make the steering sluggish and affect precision. Therefore, designers usually find a suitable compromise between the two to ensure that the vehicle's handling performance and driving comfort are well balanced.
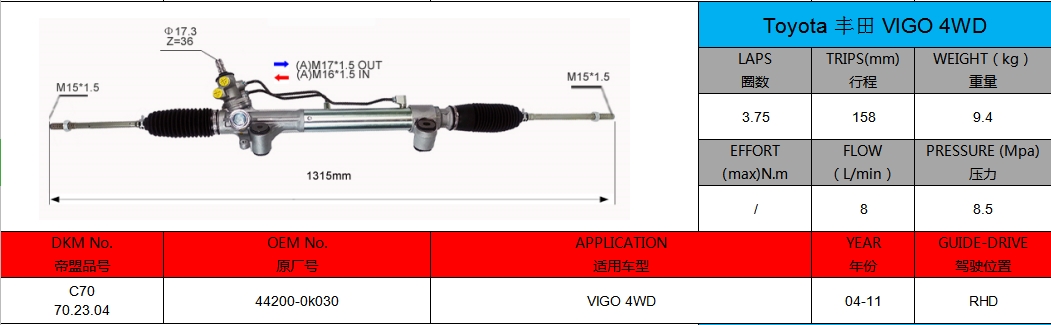
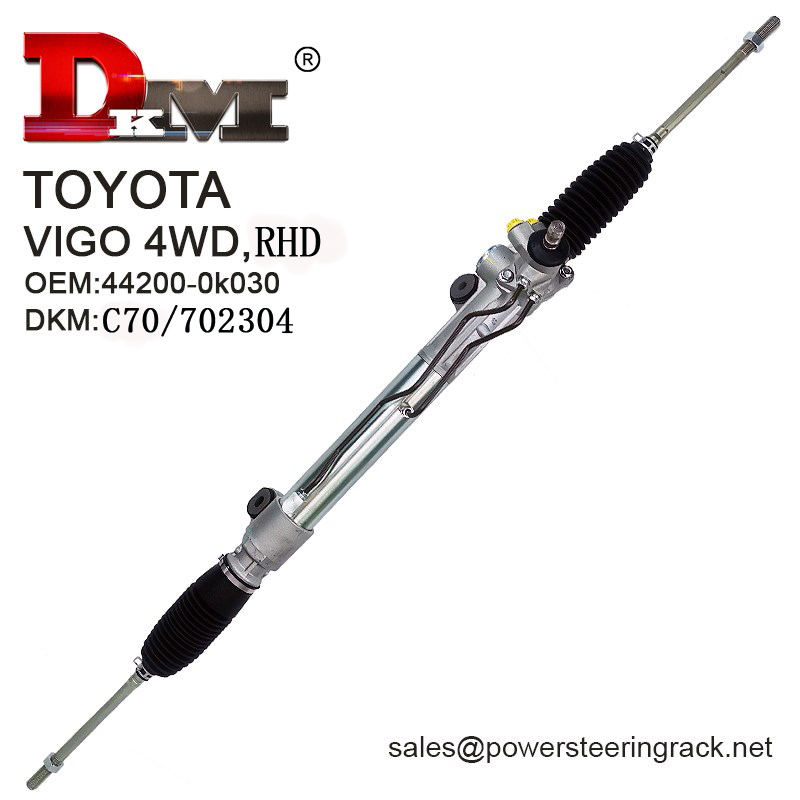
Customized Power Steering Gear Solutions from DKM
Guangdong Diamond Auto Parts Co., Ltd. (DKM) is a leading manufacturer of power steering gears, offering both standard and customized solutions to meet the needs of global automotive markets. Our products serve major brands like Toyota,
Honda, and Mitsubishi. We take pride in delivering high-quality products at affordable prices, ensuring that our customers get the best value for their money.
Whether you're purchasing in bulk or require specific modifications, DKM offers low prices, timely delivery, and reliable customer service.




